Lead Processes for the Top of Funnel
This week, we dive into refining the top-of-funnel strategy with modern lead lifecycle management. While designing a lead lifecycle varies by business, core elements remain consistent. Emerging trends in AI-driven lead scoring, intent data, and self-serve motions are reshaping traditional models. Let’s break down the key stages and their latest advancements:
Lead
Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) / Product Qualified Lead
Sales Accepted Lead (SAL)
Sales Qualified Lead (SQL)
The naming conventions may vary but generally the lead passes through several hands on the way to becoming a customer. In a marketing and sales led motion, the lead will first enter the funnel (via marketing campaign or outbound) and then handed over to sales to accept working or reject outright. In a product led motion, the prospect is already active within the product and the sales or growth team will engage with the prospect to convert to a paid plan.
Let's define each of these in more detail.
Lead
A lead is a prospect record introduced into the CRM. With AI-powered predictive analytics, sales teams can now prioritize leads based on real-time intent signals rather than static demographic data. Not all leads will be worked by sales; some may be disqualified, merged, or deleted based on enhanced AI scoring models.
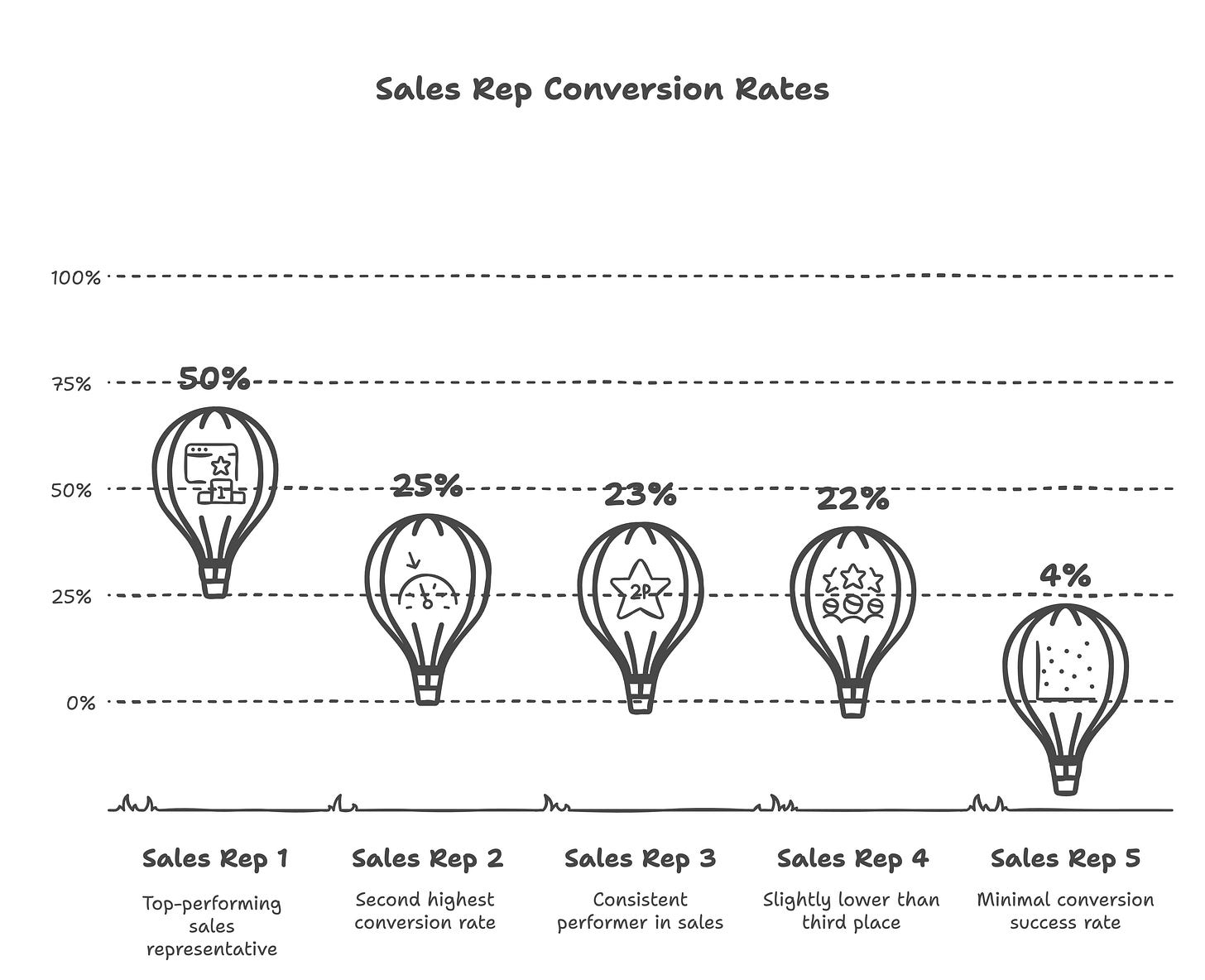
Not all leads are treated equally. Try sending your leads round robin to the sales team. I guarantee you that randomness will eventually lead to a few sales reps receiving outlandishly poor or great leads. The distribution will skew and the team will feel there is fairness built into the sales process.
Let’s say for example these were your conversion rates by rep:
Sales rep #1 must be amazing! Promote them!
Sales rep #5 must be horrible! Fire them!
But what if the game was rigged? Or that randomness took over?
Instead, try distributing leads AFTER each lead has been properly weighed and measured.
Marketing Qualified Lead
According to Gartner, a marketing-qualified lead (MQL) is a potential customer that has been reviewed by the marketing team and satisfies the criteria necessary to be passed along to the sales team.
Dimensions of an MQL include:
Geography
Persona
Industry
Employee count
Fundraising status
Complementary products used
Competing products used
Engagement score
This is where the concept of a Lead Score comes in. I touched on lead score last year here:
But let’s go over it again.
A lead score is a numerical value assigned to a lead based on their likelihood to convert into a customer. It helps sales and marketing teams prioritize leads by ranking them according to predefined criteria.
How Lead Scoring Works:
Lead scores are typically calculated using a combination of demographic, firmographic, behavioral, and intent-based factors. These scores can be rule-based (manual) or AI-driven (predictive).
Key Lead Scoring Factors:
Demographics & Firmographics
Job title
Industry
Company size
Revenue
Geographic location
Behavioral Engagement
Website visits
Content downloads
Email interactions (opens, clicks)
Event/webinar attendance
Social media engagement
Product & Intent Data
Free trial sign-ups
Product usage frequency
Pricing page visits
Competitor comparisons
Third-party intent signals (e.g., 6sense, Bombora)
Types of Lead Scoring:
Traditional Rule-Based Scoring
Assigns points based on preset rules (e.g., “+10 points for visiting the pricing page”).
Predictive Lead Scoring (AI-Based)
Uses machine learning to analyze historical data and predict conversion likelihood.
Benefits of Lead Scoring:
Helps sales prioritize high-intent leads.
Improves marketing-to-sales alignment.
Increases conversion rates by focusing on the most promising prospects.
Reduces wasted time on unqualified leads.
Product Qualified Lead (PQL)
A PQL is a lead that is already a user of your product. They may be on a free trial or a pilot. In this setup, the sales team engages with the prospect once the lead reaches certain product usage milestones. The hypothesis here is that the user has already unlocked value using the service and would benefit more by converting to a paid customer.
KPIs may include:
Logins within last 7 days
Unique users logging in
Feature usage count
Pricing page visit
Similar to an MQL score you can create a weighted dimension for the PQL.
PQL over MQL
Similar to an MQL, the sales team accepts the lead and begins working. One twist in a PLG setup is the concept of a product-based offer. Imagine a free trial user's trial is set to expire within 24 hours. In the application they receive a pop-up with a discount offer. If they upgrade today they'll receive a 20% discount. The prospect does so. In this scenario does sales even need to get involved?
Replacing MQLs with PQLs In a PLG-led motion the product does the selling for you. When done right, PLG can be an incredibly cost effective method of scaling. Revenue Operations has had to adapt quickly to the shift. In an era of an MQL based funnel the traditional model of a Lead Score threshold must shift to a Product Usage Score threshold. I believe this is far more valuable. In a Lead Scoring model the analysis focuses on optimizing for behavior and demographics. Both serve a useful function when backtesting against a historical data log. But product usage data from your paying customers will also indicate “tipping points”. These are inflections when the customer is at or near the point of which they are ready to engage. Additionally, when free trials expire it’s just as easy to display a coupon or offer right within the application. Some users are going to accept your offer. You’ve just won new business all without marketing or sales support. This is the power of PLG. At its best, it fuels growth and greatly reduces customer acquisition cost.
Sales Accepted Lead
A Sales Accepted Lead (SAL) is when sales accepts the MQL and agrees to take action. The SAL-to-MQL ratio is the first feedback loop back to Marketing on whether sales believes these leads are worth pursuing or not. Engagement can take any number of forms including:
Add into a sales sequence via sales engagement tool
Email
Call
SALs all to themselves are not a north star metric for the sales team. But they are an important barometer for the marketing team to indicate if the MQL definition is aligned with what sales deems to be a target prospect.
Sales Qualified Lead
An SQL is a lead that has met the qualification standard and a forecastable opportunity is created. Sales qualification may be defined differently from one company to the next but qualification is the process of determining whether to initiate engagement with a sales rep. If deemed so, this will bring the deal into the sales funnel. Some companies may have a pre-qualification opportunity stage which would not be an SQL. SQL is when the opportunity will be monitored and reviewed as part of the pipeline forecast. This is a real deal no matter how early they are in the sales cycle. Once the opportunity is in the funnel the business will invest attention and action into the customer to hopefully win the opportunity.
Lead Status
This differs from the Lead Status. The lead status defines where this lead is in relation to a successful sales outcome. These lead statuses are broad enough to capture most scenarios.
Lead Lifecycle and Lead Status Combinations
Lead lifecycle (stage) and status are not to be conflated. The stage determines whether or not a lead is to be worked. The status describes the status of the work.
Below is a paid framework for a lead score.
Keep reading with a 7-day free trial
Subscribe to RevOps Impact Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.